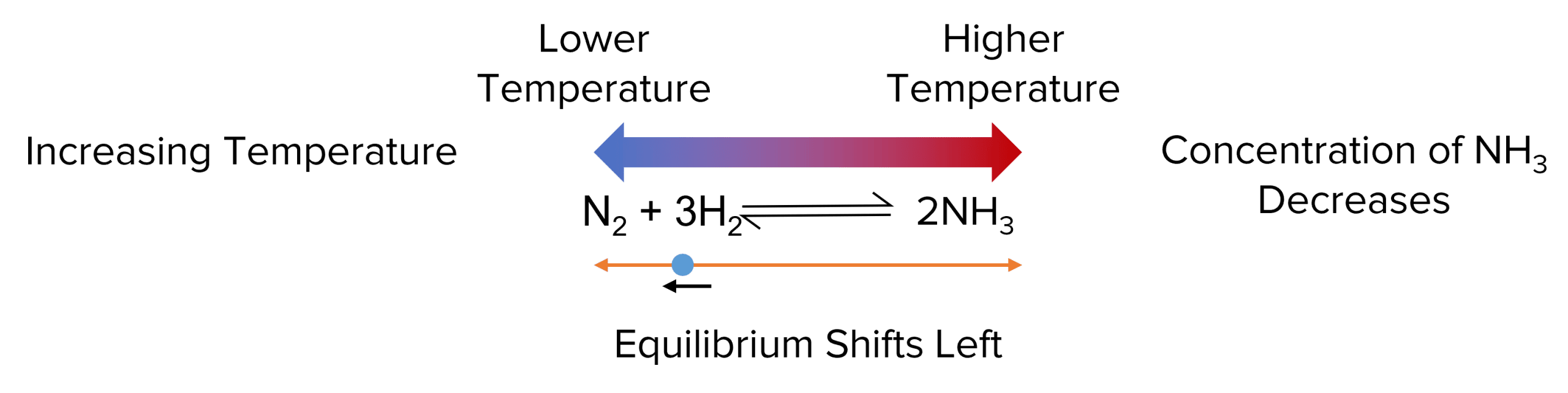
Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium . Cooling an endothermic reaction would. Anther way to view endothermic reactions is that more. cooling an exothermic reaction causes the reaction to shift toward the product side; it can be defined as: for an endothermic reaction (positive ∆h) an increase in temperature shifts the equilibrium to the right to absorb the added heat; If the equilibrium of a system is disturbed by a change in one or more of the determining factors (as temperature,. for example, if the temperature is increased for an endothermic reaction, essentially a reactant is being added, so the equilibrium shifts. suppose this reaction is at equilibrium at some temperature \(t_1\) and we raise the temperature to \(t_2\). in endothermic reactions, (\(δh>0\)) thermal energy is absorbed via the reaction. for example, if the temperature is increased for an endothermic reaction, essentially a reactant is being added, so the equilibrium shifts toward products.
from mmerevise.co.uk
in endothermic reactions, (\(δh>0\)) thermal energy is absorbed via the reaction. for an endothermic reaction (positive ∆h) an increase in temperature shifts the equilibrium to the right to absorb the added heat; cooling an exothermic reaction causes the reaction to shift toward the product side; If the equilibrium of a system is disturbed by a change in one or more of the determining factors (as temperature,. for example, if the temperature is increased for an endothermic reaction, essentially a reactant is being added, so the equilibrium shifts. Anther way to view endothermic reactions is that more. suppose this reaction is at equilibrium at some temperature \(t_1\) and we raise the temperature to \(t_2\). it can be defined as: for example, if the temperature is increased for an endothermic reaction, essentially a reactant is being added, so the equilibrium shifts toward products. Cooling an endothermic reaction would.
Reversible Reactions and Equilibrium Revision MME
Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium for an endothermic reaction (positive ∆h) an increase in temperature shifts the equilibrium to the right to absorb the added heat; Cooling an endothermic reaction would. for example, if the temperature is increased for an endothermic reaction, essentially a reactant is being added, so the equilibrium shifts toward products. for example, if the temperature is increased for an endothermic reaction, essentially a reactant is being added, so the equilibrium shifts. If the equilibrium of a system is disturbed by a change in one or more of the determining factors (as temperature,. for an endothermic reaction (positive ∆h) an increase in temperature shifts the equilibrium to the right to absorb the added heat; it can be defined as: suppose this reaction is at equilibrium at some temperature \(t_1\) and we raise the temperature to \(t_2\). Anther way to view endothermic reactions is that more. in endothermic reactions, (\(δh>0\)) thermal energy is absorbed via the reaction. cooling an exothermic reaction causes the reaction to shift toward the product side;
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Sherril Soman Grand Valley State University PowerPoint Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium for an endothermic reaction (positive ∆h) an increase in temperature shifts the equilibrium to the right to absorb the added heat; Anther way to view endothermic reactions is that more. Cooling an endothermic reaction would. cooling an exothermic reaction causes the reaction to shift toward the product side; in endothermic reactions, (\(δh>0\)) thermal energy is absorbed via. Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium.
From oneclass.com
OneClass The following diagram represents the endothermic reaction at Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium Cooling an endothermic reaction would. for example, if the temperature is increased for an endothermic reaction, essentially a reactant is being added, so the equilibrium shifts toward products. it can be defined as: suppose this reaction is at equilibrium at some temperature \(t_1\) and we raise the temperature to \(t_2\). cooling an exothermic reaction causes the. Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium.
From sciencenotes.org
Endothermic Reactions Definition and Examples Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium Cooling an endothermic reaction would. for example, if the temperature is increased for an endothermic reaction, essentially a reactant is being added, so the equilibrium shifts. it can be defined as: for an endothermic reaction (positive ∆h) an increase in temperature shifts the equilibrium to the right to absorb the added heat; If the equilibrium of a. Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium.
From revisechemistry.uk
Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions AQA C5 revisechemistry.uk Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium it can be defined as: for example, if the temperature is increased for an endothermic reaction, essentially a reactant is being added, so the equilibrium shifts. cooling an exothermic reaction causes the reaction to shift toward the product side; for an endothermic reaction (positive ∆h) an increase in temperature shifts the equilibrium to the right to. Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium.
From slideplayer.com
UNIT 6 Chemical Equilibrium ppt download Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium Anther way to view endothermic reactions is that more. Cooling an endothermic reaction would. for example, if the temperature is increased for an endothermic reaction, essentially a reactant is being added, so the equilibrium shifts. for an endothermic reaction (positive ∆h) an increase in temperature shifts the equilibrium to the right to absorb the added heat; in. Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium.
From resolutionsforyou.com
The Journey of an Endothermic Reaction Understanding the Reaction Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium it can be defined as: suppose this reaction is at equilibrium at some temperature \(t_1\) and we raise the temperature to \(t_2\). If the equilibrium of a system is disturbed by a change in one or more of the determining factors (as temperature,. for an endothermic reaction (positive ∆h) an increase in temperature shifts the equilibrium to. Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium.
From schoolbag.info
LE CHÂTELIER’S PRINCIPLE CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIUM CHEMISTRY THE CENTRAL Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium Cooling an endothermic reaction would. If the equilibrium of a system is disturbed by a change in one or more of the determining factors (as temperature,. in endothermic reactions, (\(δh>0\)) thermal energy is absorbed via the reaction. it can be defined as: Anther way to view endothermic reactions is that more. for an endothermic reaction (positive ∆h). Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chemical Equilibrium PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium for example, if the temperature is increased for an endothermic reaction, essentially a reactant is being added, so the equilibrium shifts. suppose this reaction is at equilibrium at some temperature \(t_1\) and we raise the temperature to \(t_2\). in endothermic reactions, (\(δh>0\)) thermal energy is absorbed via the reaction. for an endothermic reaction (positive ∆h) an. Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Chapter 18 “Reaction Rates and Equilibrium” PowerPoint Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium for an endothermic reaction (positive ∆h) an increase in temperature shifts the equilibrium to the right to absorb the added heat; cooling an exothermic reaction causes the reaction to shift toward the product side; Cooling an endothermic reaction would. for example, if the temperature is increased for an endothermic reaction, essentially a reactant is being added, so. Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium.
From www.studyorgo.com
How to Interpret Thermodynamics of Reactions Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium Anther way to view endothermic reactions is that more. Cooling an endothermic reaction would. for example, if the temperature is increased for an endothermic reaction, essentially a reactant is being added, so the equilibrium shifts. cooling an exothermic reaction causes the reaction to shift toward the product side; for an endothermic reaction (positive ∆h) an increase in. Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium.
From www.tes.com
Endothermic and Exothermic Temperature Changes Edexcel 91 Teaching Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium Anther way to view endothermic reactions is that more. for an endothermic reaction (positive ∆h) an increase in temperature shifts the equilibrium to the right to absorb the added heat; Cooling an endothermic reaction would. it can be defined as: in endothermic reactions, (\(δh>0\)) thermal energy is absorbed via the reaction. If the equilibrium of a system. Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium.
From wiredatatisse56wr.z22.web.core.windows.net
Endothermic And Exothermic Reaction Diagram Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium for example, if the temperature is increased for an endothermic reaction, essentially a reactant is being added, so the equilibrium shifts. in endothermic reactions, (\(δh>0\)) thermal energy is absorbed via the reaction. If the equilibrium of a system is disturbed by a change in one or more of the determining factors (as temperature,. for an endothermic reaction. Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium.
From sciencenotes.org
Le Chatelier's Principle Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium Anther way to view endothermic reactions is that more. If the equilibrium of a system is disturbed by a change in one or more of the determining factors (as temperature,. for example, if the temperature is increased for an endothermic reaction, essentially a reactant is being added, so the equilibrium shifts. Cooling an endothermic reaction would. for an. Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium.
From ar.inspiredpencil.com
Endothermic And Exothermic Reactions Temperature Change Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium cooling an exothermic reaction causes the reaction to shift toward the product side; suppose this reaction is at equilibrium at some temperature \(t_1\) and we raise the temperature to \(t_2\). Anther way to view endothermic reactions is that more. for an endothermic reaction (positive ∆h) an increase in temperature shifts the equilibrium to the right to absorb. Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium.
From wiredatasikwenzep4.z4.web.core.windows.net
Energy Diagram For Endothermic Reaction Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium suppose this reaction is at equilibrium at some temperature \(t_1\) and we raise the temperature to \(t_2\). for an endothermic reaction (positive ∆h) an increase in temperature shifts the equilibrium to the right to absorb the added heat; in endothermic reactions, (\(δh>0\)) thermal energy is absorbed via the reaction. Cooling an endothermic reaction would. for example,. Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Equilibrium PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6271487 Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium it can be defined as: If the equilibrium of a system is disturbed by a change in one or more of the determining factors (as temperature,. in endothermic reactions, (\(δh>0\)) thermal energy is absorbed via the reaction. for an endothermic reaction (positive ∆h) an increase in temperature shifts the equilibrium to the right to absorb the added. Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Thermochemistry PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3170116 Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium Cooling an endothermic reaction would. for example, if the temperature is increased for an endothermic reaction, essentially a reactant is being added, so the equilibrium shifts. in endothermic reactions, (\(δh>0\)) thermal energy is absorbed via the reaction. it can be defined as: cooling an exothermic reaction causes the reaction to shift toward the product side; Anther. Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVEDThe following reaction is endothermic 3 O2(g) ⇌2 O3(g) If the Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium for an endothermic reaction (positive ∆h) an increase in temperature shifts the equilibrium to the right to absorb the added heat; Anther way to view endothermic reactions is that more. it can be defined as: in endothermic reactions, (\(δh>0\)) thermal energy is absorbed via the reaction. Cooling an endothermic reaction would. for example, if the temperature. Endothermic Reaction Shift In Equilibrium.